42 treasury zero coupon bond
What are US "Treasury zeros" (STRIPS)? - Pecunica™ Zero-coupon notes and bonds are not issued by the US Treasury.. Instead, "Treasury zeros " are created by financial institutions and government securities brokers and dealers through the Treasury's STRIPS program.. Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of Securities (STRIPS) are synthetic zero-coupon securities that are produced by separating the interest components (TINT ... What Is the Difference Between a Zero-Coupon Bond and a Regular Bond? Zero-Coupon Bonds and Taxes Zero-coupon bonds may also appeal to investors looking to pass on wealth to their heirs. If a bond selling for $2,000 is received as a gift, it only uses...
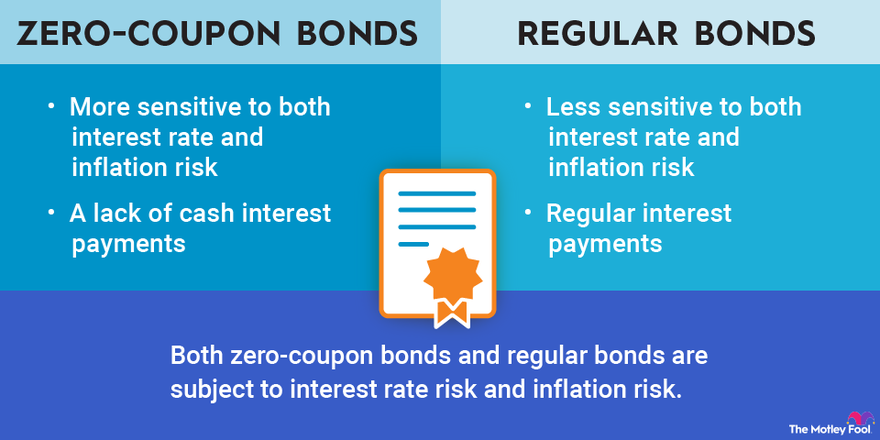
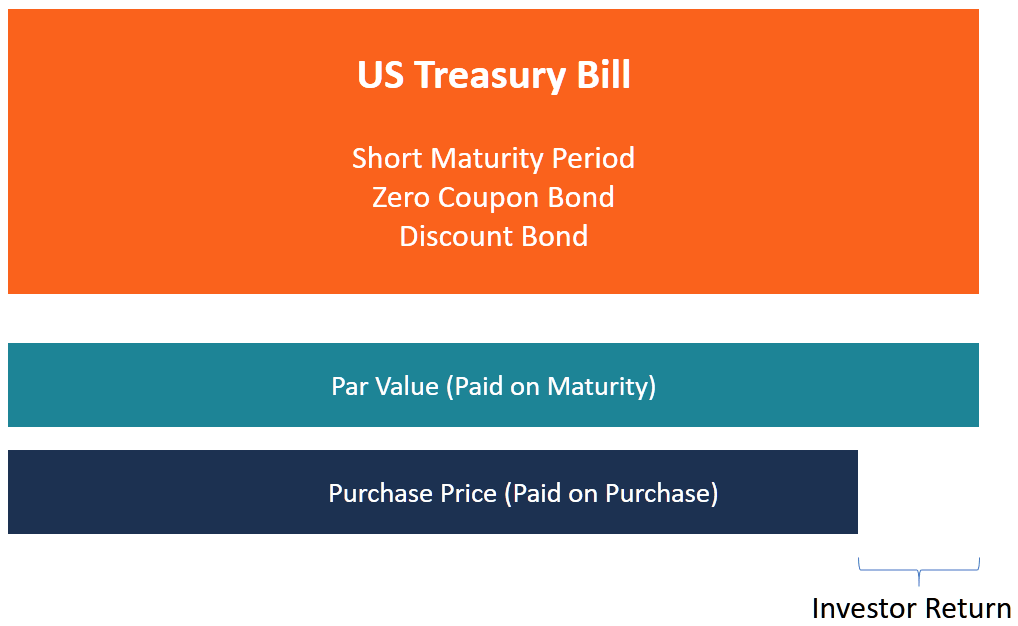
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds.

Treasury zero coupon bond
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1. Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: You must pay tax on interest annually even though you don't receive it until ... Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Let's say a zero coupon bond is issued for $500 and will pay $1,000 at maturity in 30 years. Divide the $1,000 by $500 gives us 2. Raise 2 to the 1/30th power and you get 1.02329. Subtract 1, and you have 0.02329, which is 2.3239%. Advantages of Zero-coupon Bonds Most bonds typically pay out a coupon every six months. How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks Zero coupon bonds are issued by the Treasury Department, corporations and municipalities. The bonds are considered a low-risk investment compared to stocks, commodities and derivatives....
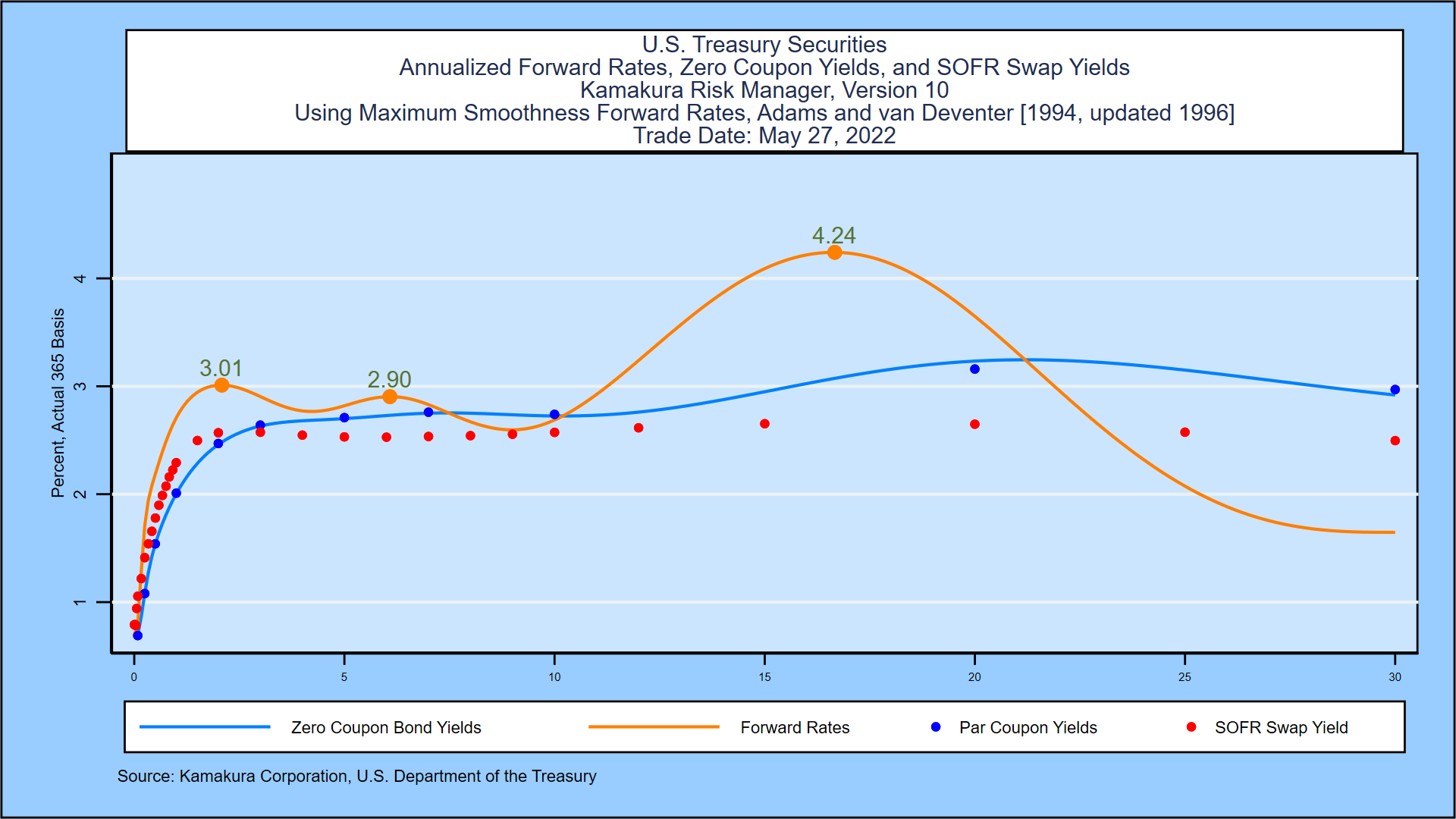
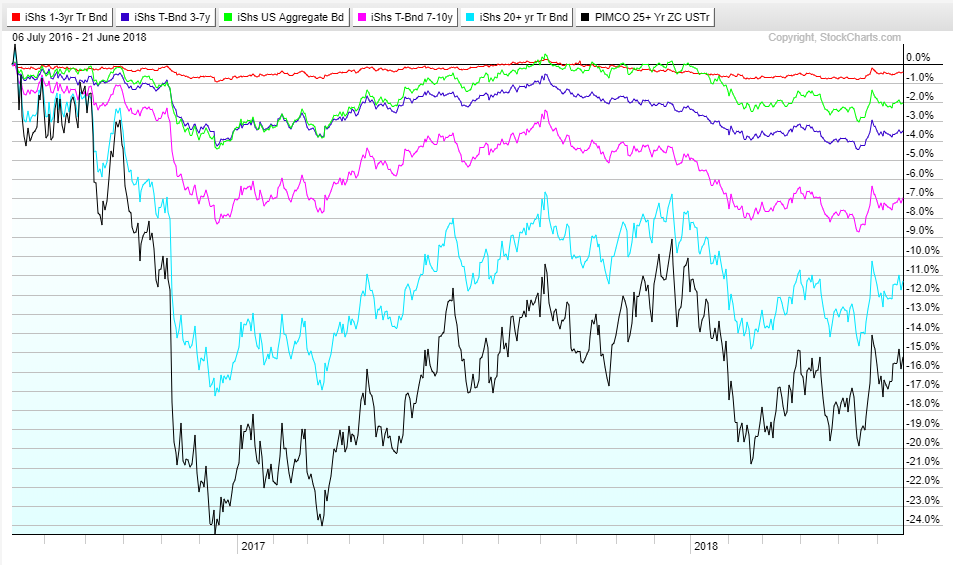
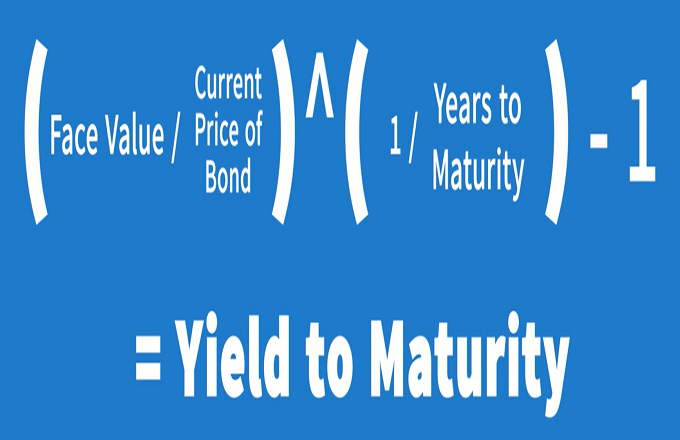
Treasury zero coupon bond. US Treasury Zero-Coupon Yield Curve - Nasdaq Nov 03, 2022 · US Treasury Zero-Coupon Yield Curve. Description These yield curves are an off-the-run Treasury yield curve based on a large set of outstanding Treasury notes and bonds, and are based on a... How to Invest in Zero-Coupon Bonds - US News & World Report PIMCO 25+ Year Zero Coupon US Treasury ETF (ticker: ZROZ ), an exchange-traded fund containing zeros with long maturities, yields about 2.7 percent. While that's not terrible compared to many... How to Calculate Yield to Maturity of a Zero-Coupon Bond Consider a $1,000 zero-coupon bond that has two years until maturity. The bond is currently valued at $925, the price at which it could be purchased today. The formula would look as... What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks As of November 2020, the current yield-to-maturity rate on the PIMCO 25+ year zero-coupon bond ETF, a managed fund consisting of a variety of long-term zeros, is 1.54%. The current yield on a...
Treasury Coupon Issues | U.S. Department of the Treasury Nominal TNC Data TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1976-1977TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1978-1982TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1983-1987TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1988-1992TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1993-1997TNC Treasury Yield Curve Spot Rates, Monthly Average: 1998 ... Zero-Coupon Bonds: Characteristics and Examples - Wall Street Prep Zero-coupon bonds, also known as "discount bonds," are sold by the issuer at a price lower than the face (par) value that is repaid at maturity. If Price > 100 "Premium" (Trading Above Par) If Price = 100 "Par" (Trading at Par Value) If Price < 100 "Discount" (Trading Below Par) Managing Risk With Fixed Income: How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds Speaking of taxes, Treasury income is exempt from state income tax but not Federal. During the economic crisis of 2008, there were many people who made a fortune in Treasury Bonds. Their long-term Treasury position became very valuable as the Federal Reserve lowered rates down to zero. As interest rates go down, the value of those bonds go up! 25+ Year Zero Coupon U.S. Treasury Index Exchange-Traded Fund - PIMCO YTM accounts for the present value of a bond's future coupon payments. PIMCO calculates a Fund's Estimated YTM by averaging the YTM of each security held in the Fund on a market-weighted basis. PIMCO pulls each security's YTM from PIMCO's Portfolio Analytics database. In general, the calculation will incorporate the yield based on the ...
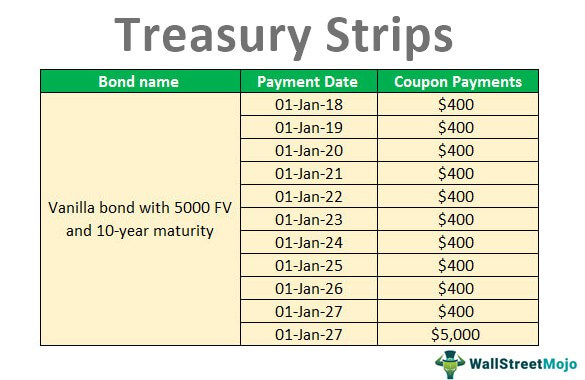
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000. Zero Coupon Bonds- Taxability Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - TaxWink The term "Zero Coupon Bond" has been defined by Section-2(48) of the Income Tax Act as below: - "Zero Coupon bond" means a bond: - (a) issued by any infrastructure capital company or infrastructure capital fund or public sector company or scheduled bank on or after the 1st day of June, 2005 (b) in respect of which no payment and benefit ... Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool For instance, a 10-year Treasury bond might have a coupon rate of 3%, meaning that each $1,000 face-value bond will make interest payments totaling $30. ... Zero coupon bonds are therefore sold at ... Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds (STRIPS) - Financial Web Zero coupon bonds are essentially the same product as all Treasury bonds, but they are paid out in a different manner. Essentially, instead of receiving the interest payments on the bond during the life of the bond, which is typical, the investor will receive the payment in full when the bond matures. This creates a product different from ...
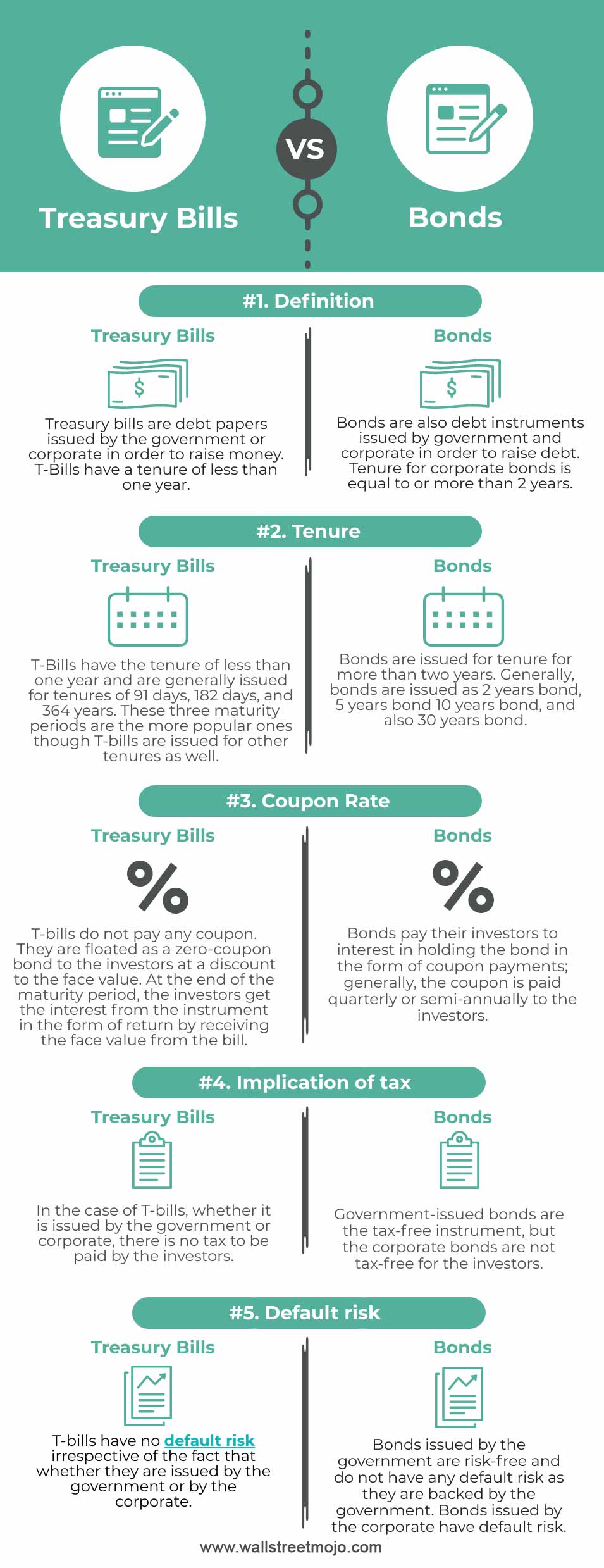
US Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity.
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - Investopedia A zero-coupon bond, also known as an accrual bond, is a debt security that does not pay interest but instead trades at a deep discount, rendering a profit at maturity, when the bond is redeemed for its full face value.
Continued Treasury Zero Coupon Spot Rates — TreasuryDirect 3.20. 3.38. 3.79. *Four quarters covering calendar year 2012 and the first and second quarters of calendar year 2013 prepared by Economic Policy (EP) using the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) legacy model. Legacy model quarterly rates can be viewed within the Selected Asset and Liability Price Report under Spot (Zero Coupon ...
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Jan 31, 2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds are also known as Treasury zeros, and they often rise dramatically in price when stock prices fall. Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds can move up...
What are Zero-Coupon Bonds? (Definition, Formula, Example, Advantages ... Mr. Tee is looking to purchase a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $50 and 5 years till maturity. The interest rate on the bond is 2% and will be compounded annually. In the scenario above, the face value of the bond is $50. However, to calculate the price that needs to be paid for the bond today, the following formula is used:
Treasury Coupon Issues and Corporate Bond Yield Curves Treasury Coupon Issues Learn about the Treasury Yield Curves for Nominal and Real Coupon Issues (TNC and TRC yield curves) and The Treasury Breakeven Inflation Curve (TBI curve). Corporate Bond Yield Curve Papers and Data Learn about the corporate bond yield curve, and how it relates to the Pension Protection Act, by downloading these papers.
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero Coupon Bond. Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
Treasury Bonds vs. Treasury Notes vs. Treasury Bills: What's the ... Note Auction: A formal bidding process that is scheduled on a regular basis by the U.S. Treasury. Currently there are 17 authorized securities dealers (primary dealers) that are obligated to bid ...
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. [1] Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value.
Treasury Coupon Bonds - Economy Watch Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not come with interest payments. Rather, the bonds are sold at prices lower than face value and their redemption is on par with the face value. Some fixed income securities such as US Savings bonds and US Treasury Bills are zero coupon bonds.
How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks Zero coupon bonds are issued by the Treasury Department, corporations and municipalities. The bonds are considered a low-risk investment compared to stocks, commodities and derivatives....
Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Let's say a zero coupon bond is issued for $500 and will pay $1,000 at maturity in 30 years. Divide the $1,000 by $500 gives us 2. Raise 2 to the 1/30th power and you get 1.02329. Subtract 1, and you have 0.02329, which is 2.3239%. Advantages of Zero-coupon Bonds Most bonds typically pay out a coupon every six months.
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1. Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: You must pay tax on interest annually even though you don't receive it until ...























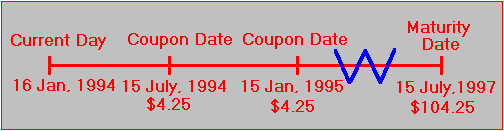

![PDF] Zero Coupon Yield Curve Estimation with the Package ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/099642ebfde435cc2d7b668516eea73c11bbd53b/13-Figure2-1.png)

Post a Comment for "42 treasury zero coupon bond"